
Maintain the pH of blood at 7.4 by decreasing or increasing the excretion of hydrogen ions Regulates the amount of fluid in the body by increasing or decreasing the urine productionĮrythropoietin (stimulates bone marrow to produce blood cells)

It participates in vital processes such as regulation of blood osmolarity and pH, regulation of blood volume and blood pressure, production of hormones, and filtration of foreign substances. The kidney is a very important organ in regards to body homeostasis. This article will discuss the anatomy and major functions of the kidney. Third kidney, horseshoe kidney, kidney agenesis, kidney stones, acute kidney failure Renal vein (drains to the inferior vena cava) Renal artery (branch of the abdominal aorta) Positioned retroperitoneally, consists of the cortex and medulla, empties urine into the ureter (which carries urine to the urinary bladder) The main function of the kidney is to eliminate excess bodily fluid, salts and byproducts of metabolism – this makes kidneys key in the regulation of acid-base balance, blood pressure, and many other homeostatic parameters.Įliminating toxic metabolites through urine, regulation of blood homeostasis and blood pressure, production of some hormones Their shape resembles a bean, where we can describe the superior and inferior poles, as well as the major convexity pointed laterally, and the minor concavity pointed medially.
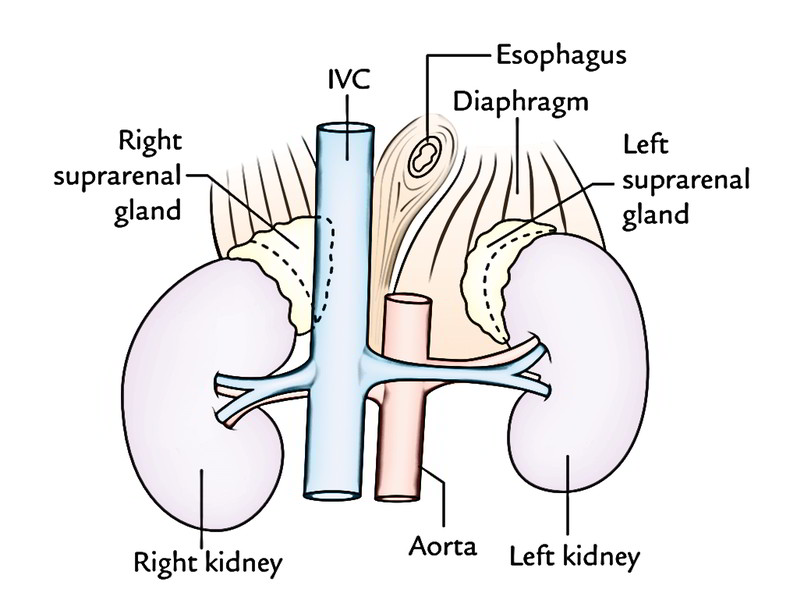
The kidneys are bilateral organs placed retroperitoneally in the upper left and right abdominal quadrants and are part of the urinary system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
